Natural-fibre composites: an overview
- Uygar Bocutoğlu

- Nov 4, 2020
- 5 min read
The global natural fibre composites market was valued at USD 4.46 billion in 2016. It is likely to register a CAGR of 11.8% from 2016 to 2024. A spiralling demand for lightweight products from the automotive industry and the growing awareness regarding green products are among the key trends strengthening market growth. However, the moisture sensitivity of these materials is poised to hinder this growth.

Tesla racecar, EPCS V2.3 Tesla P100DL, with body work in flax reinforcements (Source: Bcomp by Jaime de Diego)
Natural fibres are bio-based materials manufactured from materials such as wood, cotton, flax, kenaf, and hemp. All these materials are less harmful to the environment and easily available. The raw materials used to manufacture natural-fibre composites are environment-friendly and have the potential to replace synthetic fibres over the coming years. The rising awareness about green products, the increasing disposable income of consumers, the growing inclination towards eco-friendly products, and the urging uptake of recyclable products are likely to play a vital role in the growth of this market.
Properties of Natural-Fibre Composites (NFC) Natural-fibre composites (NFC) are 25 to 30% stronger than glass fibres of the same weight. Composites made from natural fibres help reduce the weight of components, thereby lowering total energy consumption. In addition, the NFC moulding process consumes less energy than glass fibre moulding, reducing production costs by 10%. However, their moisture sensitivity and weak bonding with polymer matrices are anticipated to hamper their growth prospects. As they absorb moisture, which results in fibre swelling, their application in the automotive industry is restricted to car interiors.
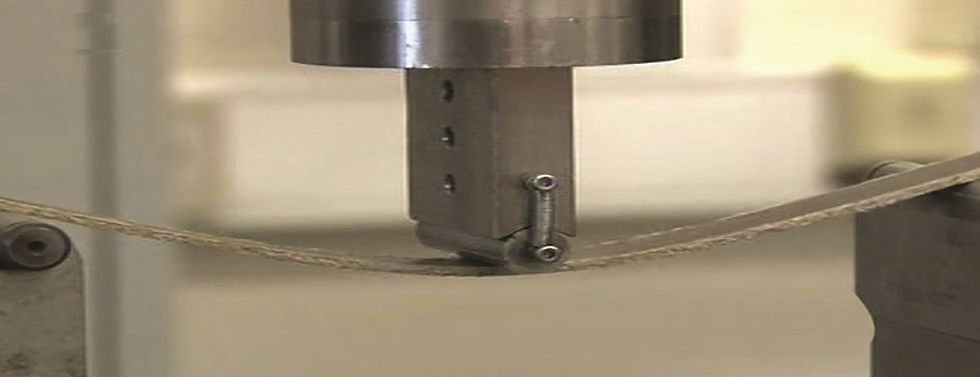
Mechanical testing of a flax-fibre composite material (Source: CELC)
Raw material insights The main raw materials for NFC are wood, flax, kenaf, cotton, and hemp. Wood has been dominating the market, accounting for 59.3% of the overall revenue in 2015. This trend is estimated to continue until 2024. The advantages of wood, including high strength and robustness, are projected to fuel its utilization over the coming years.
Flax was one of the most widely used materials in 2015, with a 13% market share. Flax is CO2 neutral, vibration dampening, and renewable as compared to carbon fibre. The advantages of flax, including high tensile strength, ultraviolet ray blocking properties, vibration absorption, and high water retention, make it one of the most widely used raw materials in the industry.
Cotton belongs to the seed fibre category, which is commonly used for textiles all over the world. Cotton is comparatively weaker than other natural fibres due to its moisture absorption properties. It can absorb moisture up to 20% of its dry weight. This market segment is expected to grow with the expansion of the textile and sporting goods industries.
The use of kenaf has been growing in various industries such as construction, oil & chemical absorbents, food packaging, and automotive. This material is highly sustainable and can be fully recycled. The surging demand for biodegradable products is likely to play an instrumental role in stimulating the growth of this market.
Hemp-based composites can replace glass fibre in many applications, and they are biodegradable. The surging demand for eco-friendly and renewable materials from the automotive and construction industries is poised to trigger this segment’s growth.

“Virgin Mojito”, IDM Marine's first boat production made of linen fiber, natural and resistant (Source: IDB Marine)
Matrix insights The matrix market is segmented into inorganic compounds, natural polymers, and synthetic polymers. Natural-polymer matrices are anticipated to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period. Due to changing lifestyles and the growing go-green trend, the rising demand for sustainable products is expected to supplement the segment’s growth.
Inorganic compounds are one of the most effective matrices in the market. They are mainly applied on wooden fibres. Inorganic compounds accounted for a 43.4% share in 2015 and this trend is anticipated to continue over the coming years. Wood fibres combined with an inorganic matrix offer benefits such as improved toughness, cracking deformation of the resulting composite, and tensile strength.
Natural polymers include starch, rubber, and synthetic polymers such as PLA and PHB (polyhydroxy butyrate). The growing demand for renewable and degradable products is projected to propel the market over the coming years. This segment accounted for 25.1% of the market in 2015.
Synthetic polymers, including thermoplastics and thermosets, are used as a matrix for wood fibres. This segment is likely to account for the second largest share over the coming years.

Hemp used as construction form in Kentucky (Source: University of Kentucky)
Technology insights In terms of technologies, the natural-fibre composites market is segmented into injection moulding, compression moulding, and pultrusion. Injection moulding requires low-molecular-weight polymers to maintain low viscosity. This process is mainly used for large-volume part production. The growing demand for large-volume production from end-use industries is poised to contribute to the growth of this segment.
Injection moulding accounted for a revenue share of 10% in 2015. It is a high-volume, high-pressure, closed moulding technology used for the development of composite products. This process is followed by two steps: preheating and pressurizing.
Compression moulding is a high-pressure, high-volume moulding technology mainly used to produce high-strength and complex objects for industries such as automotive, transportation, appliances, and other high-volume segments.
Pultrusion is widely used to produce various products for the rail transport, aerospace, boats & marine, sports goods, wind turbine blades, storage, and corrosive liquids transportation sectors. The demand for low-weight, maintenance-free, corrosion-resistant, and electrically non-conductive products is expected to support this segment’s growth.

Flax fibre processing example (Source: Procotex)
Application insights NFC are mainly used in the automotive and construction industries to manufacture door panels, seat backs, dashboards, truck liners, headliners, decking, railing, windows, and frames.
Electronics and sporting goods are promising market segments. Many products such as mobile cases, laptop cases, tennis rackets, bicycle, frames, and snowboards are also produced from natural-fibre composites.
Automobile: Natural fibre-reinforced bio-composites are used in the automotive industry to produce lightweight parts with good mechanical properties in order to improve fuel efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions. They contribute to a 30% weight reduction and a 20% cost reduction in car manufacturing. This segment accounted for a revenue share of over 30% in 2015. NFCs used in the automotive industry are developed using wood and non-wood fibres such as flax, hemp, and cellulose as an alternative to glass fibre. The resulting products are lighter compared to modern materials. Using these materials in a manufacturing process can reduce costs by approximately 20%.
Construction: Natural fibres are a low-cost, sustainable alternative to synthetic and metallic fibres used as building materials. In some cases, their mechanical properties, including impact resistance, flexural properties, and fracture toughness, are better than those of glass fibre. The construction segment held 56% of the overall market volume in 2015.
Regional insights The soaring demand for flax-based NFC, their growing popularity, and the surging demand for consumer goods are anticipated to provide a significant push to the North American market. In the region’s automotive industry, the NAFILEAN process has resulted in sustainable design for centre consoles, instrument panels, and door panels.
Extensive research is conducted by European car manufacturers to develop natural polymer matrices for front and rear door liners, boot liners, and parcel shelves. Europe accounted for 15.4% of the market volume in 2015.

Revenue of the US natural-fibre composites (NFC) market by raw materials, 2013-2024 (million USD) (Source: grandviewresearch)
Germany is one the largest producers of cars and a major hemp importer in Europe. The automotive industry’s increasing demand for biodegradable and lightweight products in order to increase fuel efficiency is estimated to stoke the country’s growth.
In the Asia Pacific region, the sporting goods, electronics, and automotive industries are projected to register a healthy growth rate in the coming years due to an increasing disposable income coupled with an improving standard of living. China is dominating the Asia Pacific market and this trend is likely to continue over the coming years.
Republished from JEC Composites.




Comments